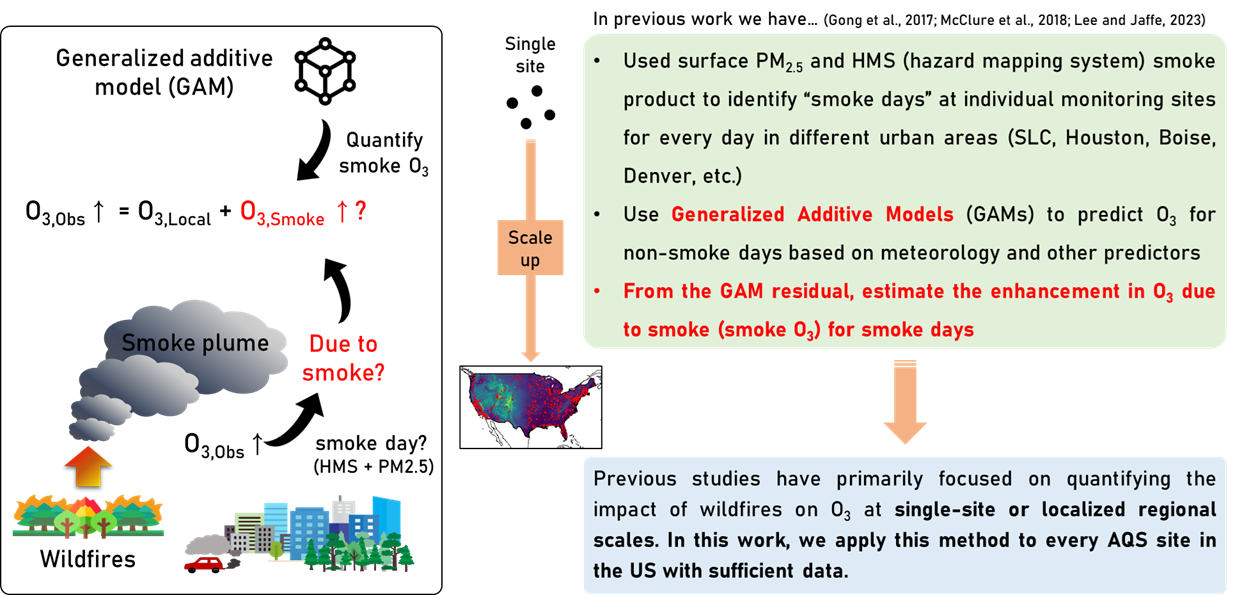
Impact of wildfire smoke on air quality in the United States
Objectives: Quantifying the impact of wildfire emissions on surface ozone
Dates of project initiation and completion: 2023.04.–present
📚 Related Publications
- Lee, H. and Jaffe, D. A.: Wildfire impacts on O3 in the continental United States using PM2.5 and a generalized additive model (2018–2023), Environ. Sci. Technol., 58, 14764–14774, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.4c05870
- Lee, H. and Jaffe, D. A.: Impact of wildfire smoke on ozone concentrations using a Generalized Additive model in Salt Lake City, Utah, USA, 2006–2022, J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc., 74, 116–130, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2023.2291197
- Jaffe, D. A., Ninneman, M., Nguyen, L., Lee, H., Hu, L., Ketcherside, D., Jin L., Cope, E., Lyman, S., Jones, C., ONeli, T., Mansfield, M. L.: Key results from the Salt Lake regional smoke, ozone and Aerosol study (SAMOZA), J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc., 74, 163–180, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2024.2301956
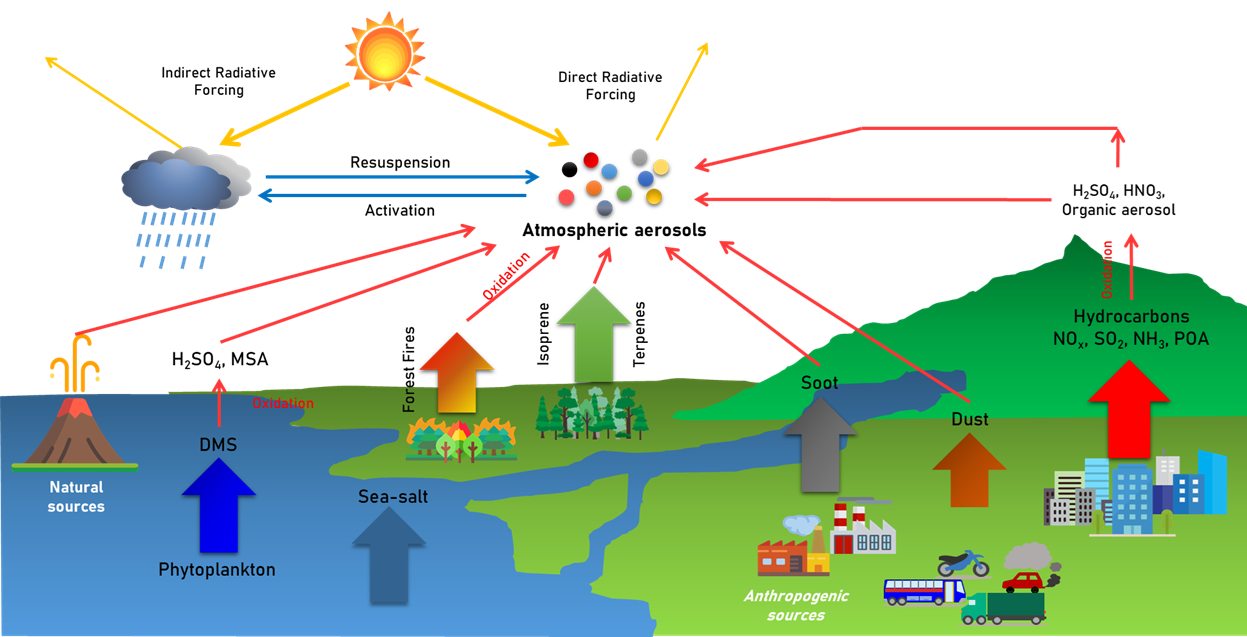
A study on the comprehensive characteristics of fine particulate matter (PM2.5): impacts, monitoring, and public health applications
Objectives:
1) Analyzing the chemical composition, sources, and transport of PM2.5 in winter haze over China and Korea and spring pollution over the Yellow Sea.
2) Developing advanced classification methods using machine learning to better understand fine particle characteristics and their health impacts.
3) Evaluating the performance and sustainability of face masks in filtering fine particles under various environmental conditions.
Dates of project initiation and completion: 2017.01.–2022.12.
📚 Related Publications
- Khadgi, J., Lee, H., Seo, J., Hong, J.-H., and Park, K.: Morphological classification of fine particles in transmission electron microscopy images by using pre-trained convolution neural networks, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 1–10, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1080/02786826.2024.2322010
- Park, M., Lee, S., Lee, H., Denna, M. C. F. J., Jang, J., Oh, D., Bae, M.-S., Jang, K.-S., and Park, K.: New health index derived from oxidative potential and cell toxicity of fine particulate matter to assess its potential health effect, Heliyon, 10 (3), e25310, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25310
- Kwak, N., Lee, H., Maeng, H., Seo, A., Lee, K., Kim, S., Lee, M., Cha, J. W., Shin, B., and Park, K.: Morphological and chemical classification of fine particles over the Yellow Sea during spring, 2015–2018, Environ. Pollut., 305, 119286, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119286
- Lee, H., Kim, S., Joo, H., Cho, H.-J., and Park, K.: A study on Performance and Reusability of Certified and Uncertified Face Masks, Aerosol Air Qual. Res., 22, 210370, 2022. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.210370
- Eom, S., Lee, H., Kim, J., Park, K., Kim, Y., Sheu, G.-R., Gay, D. A., Schmeltz, D., and Han, S.: Potential sources, scavenging processes, and source regions of mercury in the wet deposition of South Korea, Sci. Total Environ., 762, 143934, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143934
- Park, M., Wang, Y., Chong, J., Lee, H., Jang, J., Song, H., Kwak, N., Borlaza, L. J. S., Maeng, H., Cosep, E. M. R., Denna, M. C. F. J., Chen, S., Seo, I., Bae, M.-S., Jang, K.-S., Choi, M., Kim, Y. H., Park, M., Ryu, J.-S., Park, S., Hu, M., and Park, K.: Simultaneous measurements of chemical characteristics and oxidative potential of fine particles during winter haze period in urban sites in China and Korea, Atmosphere, 11, 292, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11030292
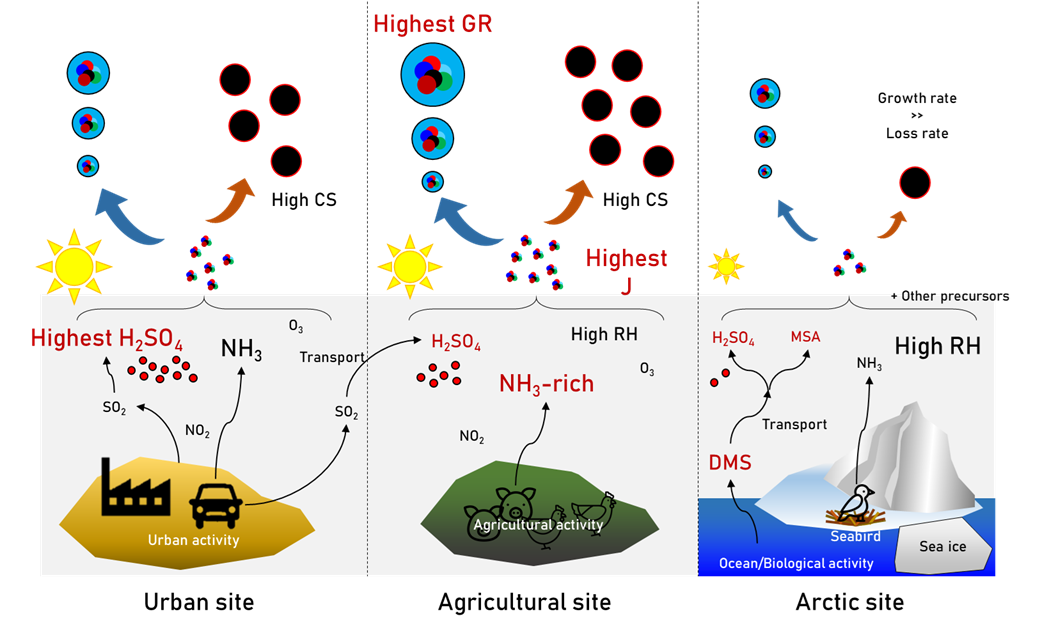
A study on new particle formation (NPF) in the ambient atmosphere in various environments
Objectives: Identifying differences of characteristics and governing factors for the NPF among sites
Dates of project initiation and completion: 2018.01.–2022.12.
📚 Related Publications
- Lee, H., Cho, H., Kim, J., Yoon, Y. J., Lee, B. Y., and Park, K.: Comparison of new particle formation events in urban, agricultural, and Arctic environments, Atmos. Environ., 120634, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2024.120634
- Lee, H., Lee, K., Krejci, R., Fiebig, M., Lunder, C. R., Aas, W., Park, J., Park, K.-T., Lee, B. Y., Yoon, Y.-J., and Park, K.: Atmospheric new particle formation characteristics in the Arctic as measured at Mount Zeppelin, Svalbard, from 2016 to 2018, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 20, 13425–13441, 2020. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-20-13425-2020
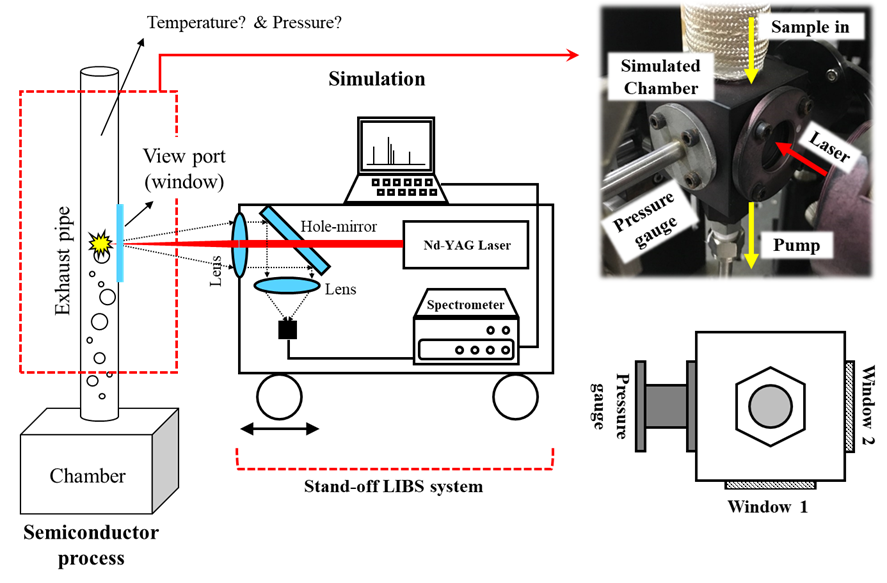
Development of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) system and its application in aerosol detection and industry fields
Objectives: Exploring the potential of LIBS technique in analyzing elements in flowback water from fracking operations and in detecting contamination particles in industrial processes
Dates of project initiation and completion: 2017.03.–2020.02.
📚 Related Publications
- Lee, H., Kim, G., Kim, H.-A., Maeng, H., Park, H., and Park, K.: Application of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for detection of elements in flowback water samples from shale gas wells, Applied Optics, 59, 2254–2261, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.381687
- Kim, G., Kim, K., Maeng, H., Lee, H., and Park, K.: Development of Aerosol-LIBS (Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy) for Real-time Monitoring of Process-induced Particles, Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 19, 455–460, 2019. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2018.08.0312
- Lee, H., Maeng, H., Kim, K., Kim, G., and Park, K.: Application of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for real-time detection of contamination particles during the manufacturing process, Applied Optics, 57 (12), 3288–3292, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.57.003288
- Maeng, H., Chae, H., Lee, H., Kim, G., Lee, H., Kim, K., Kwak, J., Cho, G., and Park, K.: Development of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) with times ablation to improve detection efficiency, Aerosol Science and Technology, 51, 1009–1015, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1080/02786826.2017.1344352